|
|
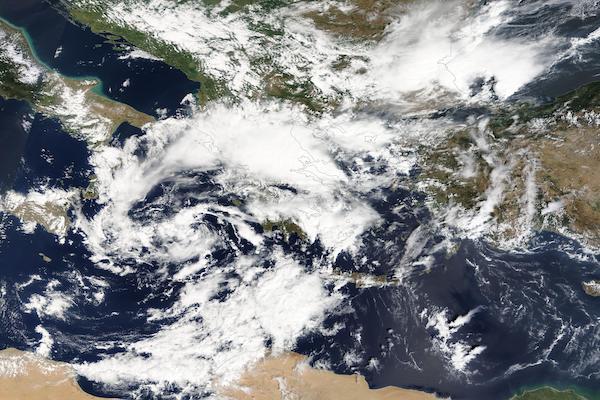
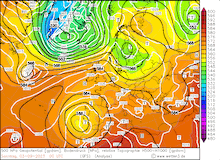
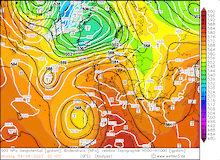
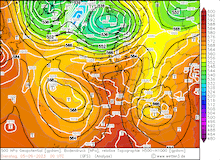
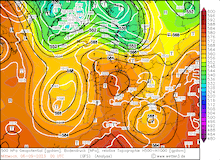
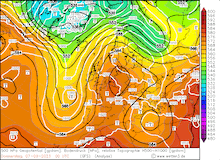
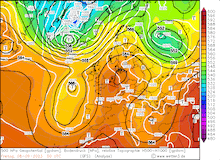
From September 04, 2023, to September 07, 2023, the accumulated precipitation totals reached more than 500 mm at many locations across the central part of Greece. At Zagora, the re-reported precipitation data suggests that the storm-related precipitation totals reached 1096 mm. The second-highest precipitation total was observed at the weather station in Portaria recording 885 mm of rain, though due to a suspected power outage, the weather station recorded no data on September 06, 2023.
|
|
|
|
|
|
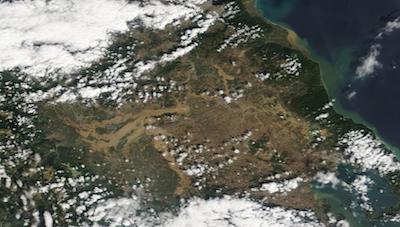
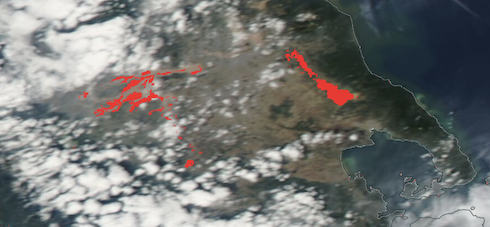
| Visible Satellite Imagery of the central part of Greece (left), 08.09.2023, and satellite-based reconaissance of flooded areas in the central part of Greece (right), 09.09.2023, source: NASA Worldview | ||
 |
 |
|
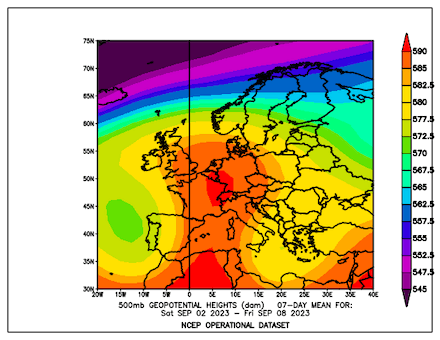
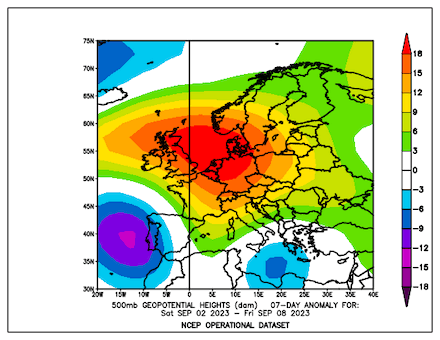
Ultimately, the precipitation totals by Storm Daniel are the worst in the recorded history of Greece and correspond to more than the average annual precipitation in this region. The special synoptic pattern over the Eastern Mediterranean and the well-above-average ocean temperatures of the Aegean Sea provided the environment for the extreme precipitation in the coastal regions of Thessaly and Central Greece. The remarkable marine heat wave in the Mediterranean this year will have likely contributed to these precipitation totals, by providing enhanced moisture fluxes.
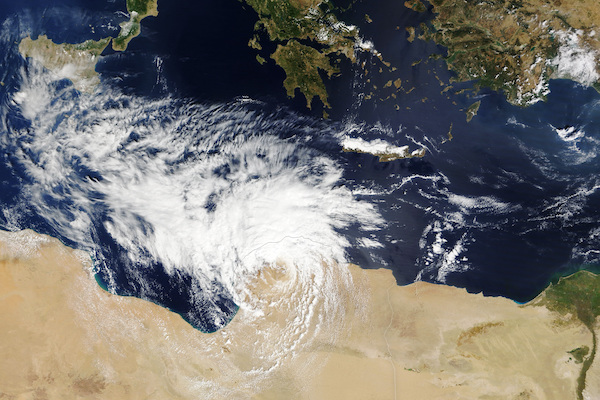
Flooding Libya - September 10, 2023 After causing severe flooding in Central Greece, storm Daniel moved over the Mediterranean. Over the warm waters of the Mediterranean with sea surface temperatures of up to 27 °C off the coast of Libya, the surface low intensified considerably. Over the open ocean, the structure of the storm started resembling the structure of a tropical cyclone, as the storm developed a shallow warm core. These cyclones are called Medicane as their structure is a mixture of a mid-latitude cut-off low and a tropical cyclone. In the Mediterranean, these storms form most often during the autumn months, when troughs from the mid-latitudes reach the Mediterranean and form cut-off lows. Due to the substantial diabatic heating of the warm ocean waters of the Mediterranean, these low-pressure systems can develop tropical characteristics.
|
Visible Satellite Imagery of Storm Daniel showing tropical characteristics as the storm made landfall in Libya, 10.09.2023, source: NASA Worldview | ||
 |
||
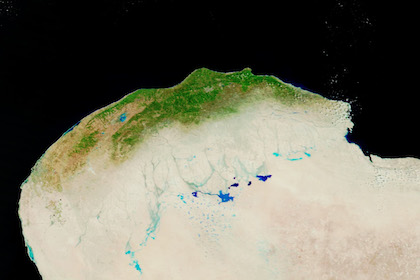
On September 10, 2023, storm Daniel reached the coast of Libya, bringing torrential downpours to the coastal region of Cyrenacia in Libya. The city of Al Bayda received 414 mm of rain within a 24 h-period. Normally, the coastal regions of Libya receive only a few millimeters of rain in September. Further, inland satellite images after the passage of Storm Daniel show standing water in the desert of Libya because of the extreme precipitation. The comparison of satellite imagery before and after the passage of Storm Daniel shows that the vegetation in the coastal regions of Libya is much greener than before.
| Visible Satellite Imagery of Northern Libya before (right), 07.09.2023, and after the passage of Storm Daniel (left), 13.09.2023, source: NASA Worldview | ||
 |
 |
|
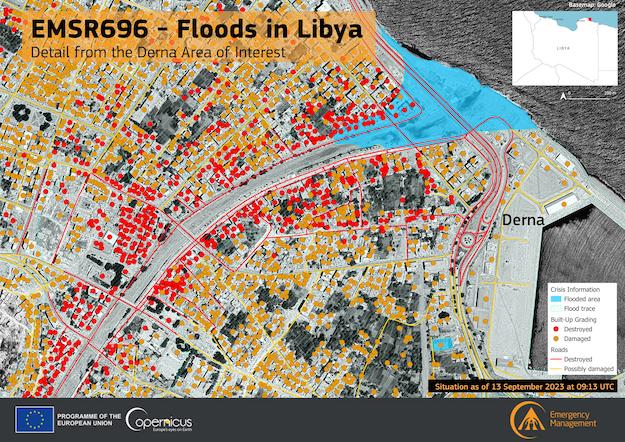
The port of Derna received more than 100 mm of rain during the passage of storm Daniel, normally Derna receives only 1.5 mm of rain in September. As a result, one of the most devastating floodings of the new millennium occurred, as two dams along the normally dry Wadi Derna collapsed and brought extreme flooding to the city. Many residential buildings were swept away as the flood water inundated the city, as the Wadi Derna runs straight through the city.
|
Damaged and destroyed buildings in the port Derna in Libya after the flooding of the Wadi Derna, 10.09.2023, source: Copernicus - Image of the day, Credit: European Union, Copernicus Emergency Management Service data | ||
 |
||
Nearly 4,000 buildings were damaged or destroyed because of the flooding. More than 5,000 confirmed fatalities were reported from the city, with more than 10,000 people still missing. Estimates say that up to 20,000 people might have lost their lives as the flood wave moved through the city. Reports suggest that in the war-torn country, neglect has led to the failure of the two dams upstream of Derna along the Wadi Derna. Nevertheless, the precipitation totals due to Storm Daniel in parts of Libya were unprecedented, especially in a month when the country receives hardly any precipitation.
Text: KG
September 09, 2023
updated:
KG
September 20, 2023