|
At the beginning of February several storm lows swirled over Europe and Germany. One of them was fast-running UWE. It was a Shapiro-Keyser cyclone which brought
gusts up to 148 kph (Feldberg / Black Forest) on 10 February 2019. Particularly affected were the south of Rhineland-Palatinate, Baden-Württemberg and Bavaria.
Trigger of the gusts was the strong pressure gradient, as well as the passage of the cold front.
Development of the low pressure Systems
No less than three winterstorms whirled through Europe at the beginning of February. STEFAN launched the storm series on 06/07 February 2019
and brought gusts up to 117 kph, especially in the UK. THOMAS followed a day later, causing storms in both the UK and northern Germany.
|
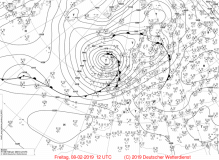
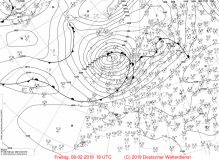
Sea level pressure, 08 Feb till 10 Feb |
Source:
wetter3.de
|
 |
 |
 |
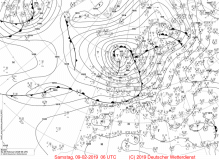 |
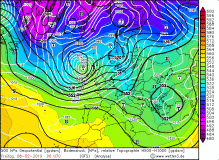
THOMAS got through an explosive cyclogenesis on 08 February as it wandered across the Atlantic to the east. Its core pressure dropped by
30 hPa in 24 hours. The reason for this was the favorable position in the jet stream in the region of positive divergence and positive vorticity
advection at the left jet exit. With a core pressure of 965 hPa it reached Irland and Scotland at noon of 08 February. On the west coast of Scotland gusts
up to 164 kph (Aonach Mor) were recorded. After reaching Great Britain and Ireland, THOMAS 'speed of deceleration slowed significantly and its center remained
longer north of Scotland. The gale-force wind continued into the night and the next morning. Although THOMAS did not move through Germany, its cold front caused
on the coasts stormy gusts up to 74 kph, in the low mountain range 133 kph (Feldberg / Black Forest). On 09 February At the southwestern flank of THOMAS, a
convergence line was formed. Showers and thunderstorms were the result and stormy precipitation. Local measured barely 60 mm in 24 hours.
|
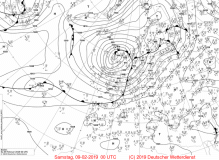
500hPa geopotential with sea level pressure and 300 vorticity advection, 08 Feb |
Source:
wetter3.de
|
 |
 |
 |
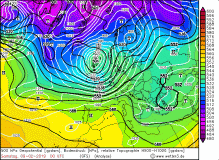 |
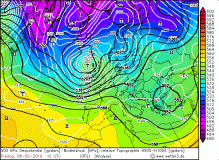
On the same day, the storm depression UWE developed on the Atlantic. As a wave disruption, it moved quickly east. In the evening, its
center reached the Bay of Biscay and the core pressure began to fall. Although its displacement speed decreased slightly, the pressure gradient
increased mainly on the southwest flank. With a core pressure of 988 hPa, UWE reached Northern Germany on the morning of 10 February.
|
500hPa geopotential with sea level pressure, pseudopotential temperature and 300 vorticity advection 10 Feb |
Source:
wetter3.de
|
 |
 |
 |
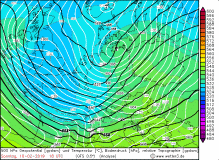 |
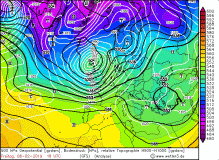
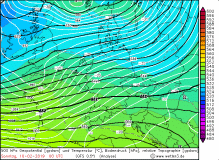
First storm gusts
up to 119 kph reached from noon the southwest of Germany. Compared to the forecasts, the gusts were weaker and the main storm field was much smaller. The warm
front, which is characterized by its massive clouds at Shapiro-Keyser cyclones, reached the west and north of Germany already in the morning hours and brought
to noon moderate rainfall. Due to strong warm air advection and the associated extremely mild temperatures this fell out as rain. Especially in the south,
the thermometer climbed to around 14 ° C in Lahr or Stuttgart-Echterdingen.
|
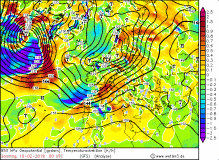
850 hPa temperature advection and precipitation, 10 Feb |
Source:
wetter3.de
|
 |
 |
 |
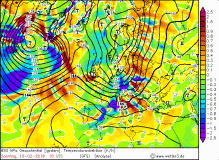 |
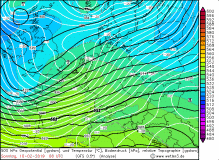
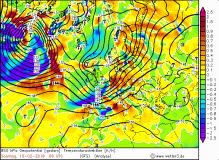
The cold front and thus the second wind maximum reached the west of Germany
at 16:00 CET and also brought precipitation in form of strong showers. Due to the western dam high precipitation amounts came together in the German low
mountain ranges (Brocken 62 mm / 24h). Gale gusts up to 148 kph were also involved in the passage of the cold front. The cold front brought stormy gusts till
night in Baden-Württemberg and Bavaria. Also the following day it remained stormy in most parts of Germany due to showers.
Due to the horizontal pressure gradients of about 4 hPa/100km occurred
over Germany. This resulted in high wind speeds as well as storm and gale-force gusts.
Measured wind gusts (selection), data source: Meteociel
| Location |
Wind Gusts in kph |
Date |
Feldberg/Schwarwald
Brocken
Zugspitze
Hornisgrinde
Wasserkuppe
Weilheim-Bierbronnen
Weinbiet
|
148
137
133
113
112
112
109
|
10 Jan
10 Jan
10 Jan
10 Jan
10 Jan
10 Jan
10 Jan
|
|
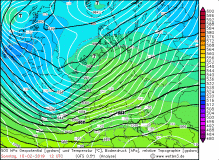
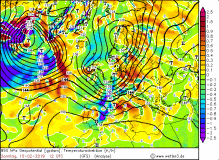
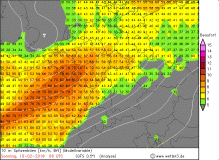
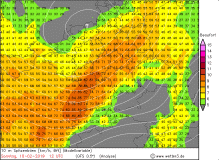
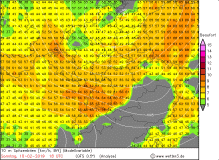
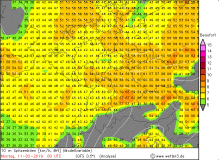
UWEs peak gusts in 10m (modell) |
Source:
wetter3.de
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|