|
Abundant precipitation in December brought extensive flooding to the Northern German Lowlands with many river basins running at decadal flooding levels. River flooding was especially severe along the Harz mountains draining into the Weser River. Minor flooding was observed in the Rhine River basin, with multiple 2-year floods occuring in December 2023 and early January 2024.
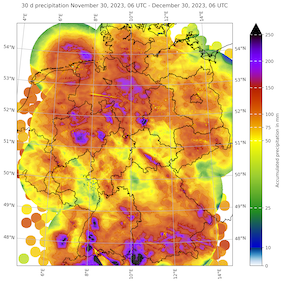
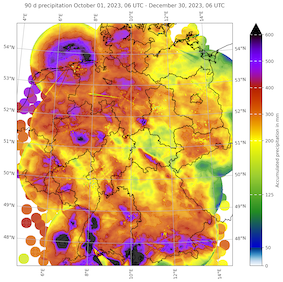
An unusually persistent and active weather pattern affected Central Europe since the second half of October 2023, bringing abundant precipitation to many regions in Central Europe. In regions with enhanced orographic lift, the period between the second half of October 2023 to the beginning of January 2024 brought up to 1000 mm of precipitation. Especially, in Lower Saxony the year 2023 had already been very wet, with the abundant rains in the last weeks of the year 2023 bringing the year precipitation totals to more 150 % of the annual precipitation. With a state average of nearly 1100 mm, 2023 became the wettest year on record in the state of Lower Saxony, with many stations outside the state in Northwestern Germany recording the wettest year on record too.
|
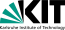
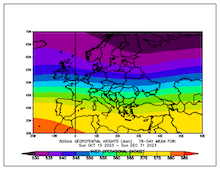
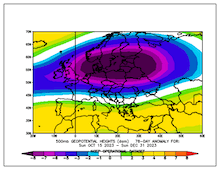
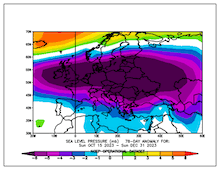
500 hPa Geopotential mean and anomaly (the two plots on the left), mean and anomaly of the mean sea level pressure (the two plots on the right) over Europe, 15.10.2023 - 31.12.2023, source:
PSL NOAA
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
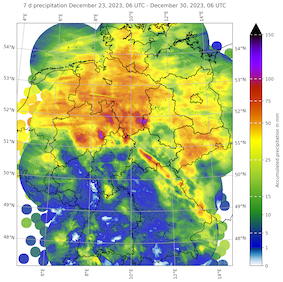
The flooding event was induced by a week-long period of abundant precipitation, with the highest precipitation totals recorded along the westward-facing slopes of the Harz mountains. The station Braunlage in the Harz mountains recorded 308.8 mm of precipitation in the period from December 19 to December 29, 2023. Due to the unusually wet year the soils in most areas were already saturated preceding this intense precipitation event. As a result, most of the precipitation was forced to drain directly into the river basins as surface run-off.
|
7-day (left), 30-day (middle), and 90-day precipitation over Germany, 30.12.2023 06 UTC, source:
DWD, Visualization: K. Gramlich
|
 |
 |
 |
Over the Christmas Days of 2023, a strong flood developed along the rivers draining the Harz and Sauerland mountains. As flooding crests of many rivers feeding into the Weser River were superimposed onto each other, a long-lasting flood crest was observed along the Weser River in Lower Saxony. Due to the flat terrain in most parts of Lower Saxony, large areas were inundated by the flooding. Especially at the confluence of the rivers Leine and Aller, severe flooding was observed in the region around Hannover, where the river levels of the Leine surpassed the 6-meter mark. These water levels are close to the all-time high water levels recorded since the Second World War.
|
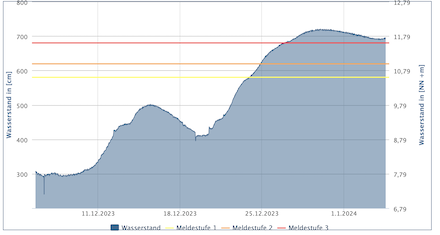
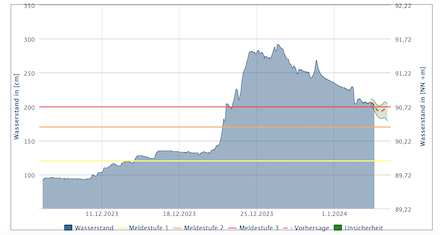
30-day water levels at Inschede along the Weser River (left) and at Schladen at the Oker River (right), 04.01.2024, source:
NLWKN Niedersachsen
|
 |
 |
Along smaller rivers in the Harz mountains, the river flooding was intensified by very full mountain reservoirs, which were not able to dampen the river levels by storing excess water in the reservoirs and releasing it at a later point in time. The water levels in the reservoir were already elevated by the wet autumn in this region, forcing a much higher water release from the reservoirs. As a result of the prolonged flooding event, many levees in Lower Saxony have become soft due to water entrainment weakening the levees. In some areas in Lower Saxony, evacuation orders were put into place where the risk of a levee failure was given.
In the Rhine Basin, the severity of the river flooding was much less severe. Multiple episodes of flooding were recorded from late November 2023 into early January 2024. However, all flood crests reached approximately a 2-year flood. Nevertheless, some residential areas were inundated. With a substantial snowpack in the Swiss Alps and well-above-average water levels in Lake Constance, the risk of another flooding event along the Rhine River cannot excluded in the next months until early summer.
In Lower Saxony, a cold spell beginning in the next week brings the risk that the vast flooded areas could freeze over as the potential for a prolonged period of temperatures below or near the freezing mark is given.
Text: KG
January 04, 2024
|