|
Super Typhoon YAGI was the first category 5-equivalent typhoon to form over the Western Pacific Basin this year. Furthermore, it is only the second category 5 tropical cyclone to form this year globally. Super Typhoon YAGI made landfall in the Northern Philippines, the Hainan Island, and Northern Vietnam. At peak intensity, Super Typhoon YAGI had 1 min-sustained winds of up to 260 kph and a minimum central pressure of 916 hPa.
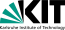
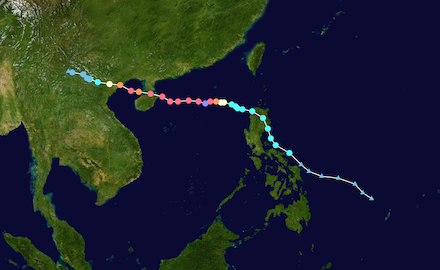
The tropical depression which would mature into Super Typhoon YAGI formed on August 30, 2024, over the warm waters of the Philippine Sea between the Philippines and Palau Islands. During the formation of the tropical disturbance, the sea surface temperatures (SSTs) in the Philippine Sea were around 30 °C. These water temperatures are highly conducive for tropical cyclone formation. Initially, the development of the tropical disturbance was slow. The system only slowly strengthened into a tropical cyclone before making landfall on the main island of the Philippines, Luzon, on September 02, 2024.
|
Track of Super Typhoon YAGI (left), source: NASA, and the SSTs over the Pacific, 30.08.2024 (right), source:
NOAA Coralreefwatch
|
 |
 |
While traversing the island from east to west on September 02, 2024, the tropical storm brought torrential rains to the islands. Due to the heavy rains, river and flash flooding were observed on the affected islands. Though the winds of the system were rather weak by tropical cyclone standards, widespread damage to homes and crops was reported. After the entire system moved offshore over the warm waters of the South China Sea, the tropical cyclone could again strengthen. Once more, the tropical cyclone was over warm waters of the South China Sea with SSTs of around 30 °C. The tropical cyclone slowly moved eastwards across the South China Sea. By September 04, 2024, the tropical cyclone YAGI reached typhoon status with sustained winds of more than 120 kph.
|
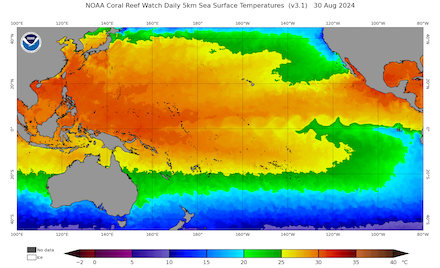
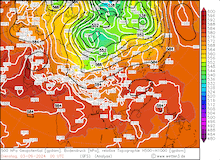
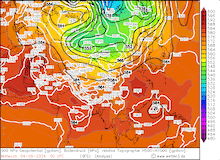
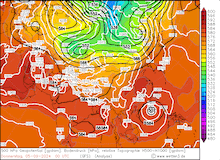
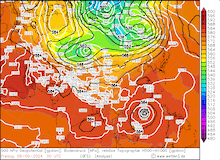
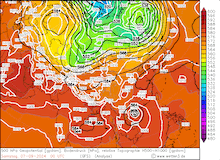
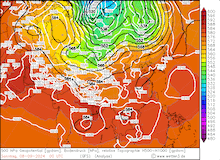
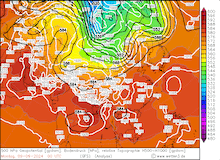
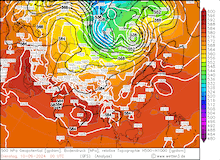
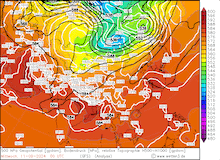
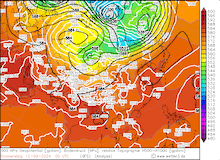
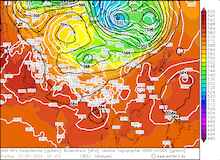
500 hPa geopotential, 1000 hPa to 500 hPa thickness, and sea-surface pressure over Asia, 02.09.2024 00 UTC - 13.09.2024 00 UTC, source:
wetter3.de
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Within a 24 h period, Typhoon YAGI intensified from a category 1-equivalent typhoon into a super typhoon due to very favorable environmental conditions. By September 05, 2024, 00 UTC, Super Typhoon YAGI had 1 min sustained winds of 260 kph. All the while, the central pressure of Super Typhoon YAGI dropped by 55 hPa/24 h. This is one of the strongest rapid intensifications of a tropical cyclone observed in recent years. Throughout September 05, 2024, Super Typhoon YAGI underwent an eyewall replacement cycle. Due to the eyewall replacement cycle, the tropical cyclone slightly weakened.
Crossing the South China Sea, Typhoon YAGI neared Hainan Island on September 06, 2024. After the eye wall replacement cycle of Typhoon YAGI had finished, the tropical cyclone had once again intensified into a super typhoon with category 5-equivalent 1 min-sustained winds of up to 260 kph. By 08 UTC on September 06, 2024, Super Typhoon YAGI made landfall on the northernmost part of Hainan Island as a category 4-equivalent tropical cyclone with 10 min-sustained winds of 230 kph. Upon landfall, Typhoon YAGI had a large eye with a diameter of nearly 40 km. The Hainan Island and the Leizhou Peninsula were battered with violent winds and torrential downpours. Coastal measuring sites on the Hainan Peninsula recorded wind gusts of up to 160 kph.
|
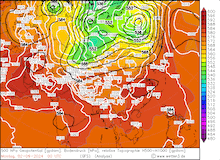
Daily development of Super Typhoon YAGI over the South China Sea captured by visible satellite imagery, 05.09.2024 - 08.09.2024, source:
NASA Worldview
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
After passing Hainan Island, Typhoon YAGI weakened into a category 3-equivalent tropical cyclone with 10 min-sustained winds of around 200 kph. Over the Gulf of Tonkin, the warm waters allowed Typhoon YAGI to retain its intensity before making landfall in Northern Vietnam on September 07, 2024. Typhoon YAGI made landfall in the famous Ha Long Bay in Northern Vietnam with 10 min-sustained winds of 200 kph. Upon landfall, Typhoon YAGI brought a very strong storm surge, torrential rains, and violent winds. Further inland, Typhoon YAGI moved across the metropolitan area of Hanoi. Over the mountain ranges of Southeast Asia, the tropical cyclone quickly weakened. Nevertheless, the torrential rains in the mountain ranges of Southeast Asia brought widespread precipitation totals of more than 400 mm. Local precipitation totals of more than 800 mm were reported with tropical cyclone YAGI. These rains lead to severe to catastrophic river flooding in parts of Vietnam and Myanmar.
Interestingly, the upper-level circulation of Typhoon YAGI remained intact while the system slowly moved across Southeast Asia. By September 14, 2024, the remnants of this circulation merged with the upper-level circulation of the monsoon system over the Indian Subcontinent. Moreover, Super Typhoon YAGI was only the fourth super typhoon observed over the South China Sea since record-keeping began.
More than 500 fatalities have been reported with Super Typhoon YAGI with most of the fatalities being reported from Vietnam and Myanmar. Due to the proximity of the track of Super Typhoon YAGI to the southern part of Mainland China with its large metropolitan areas, large insured damages have been reported. Adjusted to 2023 USD, Super Typhoon YAGI was the sixth costliest tropical cyclone in the Pacific basin with an insured damage of 14 billion USD. Around 85 % of these damages have been reported by China, with the remaining part of the damages mostly occurring in Vietnam.
Text: KG
September 18, 2024
|