|
A strong trough over the western part of the US led to significant snowfall events between 08.12 and 12.12.2022 along the Sierra Nevada Mountain range and the highest altitudes of the Coastal Mountain ranges of Northern California.
On Thursday, 08.12.2022, a surge of cold air over the Eastern Pacific led to the amplification of a trough over the Eastern Pacific shifting eastwards over the western part of the US. This enhanced southwesterly flows along the eastern flank of the trough. The airflow must lift over the mountain ranges in California, leading to a strong orographic lift, as the coastal mountain ranges reaches up to 2.400 m in Northern California. Further, the mountains in the Sierra Nevada reach up to over 4.000 m altitude exacerbating the orographic lift. Especially the central part of the Sierra Nevada is so aligned that oncoming southwesterly winds hit the mountain range nearly perpendicular. Over the Eastern Pacific the subtropic southwesterly current can pick up a lot of moisture, causing in combination with orographic lift intense orographic precipitation along the western flanks of the mountain ranges.
|
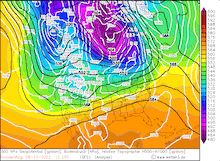
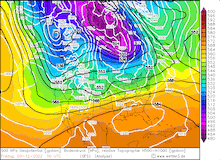
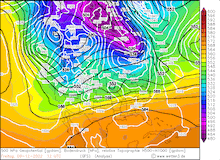
500hPa Geopotential and sea level pressure North America , 08.12.2022 12 UTC - 12.12.2022 00 UTC, source:
wetter3
|
 |
 |
 |
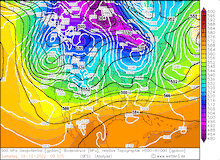 |
The eastward moving trough caused the first snow event along the Californian mountains on Friday, 10.12.2022, with fresh snow accumulations of up to 30 cm at the western flanks of the Sierra Nevada. On Friday Afternoon a strong surface low intensified as an upper-level trough moved over the system, enhancing the pressure gradient over the western part of the US. The exacerbated southwesterly current brought very moist air masses into California, leading the severest snow fall event of this winter season so far. On the warm side of the system the snow line rose above 2000 m. With colder air masses shifting southwards the snow line subsequently fell below 1500 m in the latter stages of Saturday. Snowfall continued into Sunday, 11.12.2022, with alternating intensity and decreasing snow line, diminishing into local snow showers.
At higher altitudes with strong orographic lift, snow accumulations of up to 1,50 m at W Truckee were observed from the snowstorm on Saturday, 11.12.2022. Precipitation totals of this event surpassed 100 mm at the western flanks of the Sierra Nevada, while over 50 mm of rainfall was observed in parts of the Central Valley. The system caused massive disruptions in the cross traffic through the Sierra Nevada with closure along the important roadways of Interstate 80 or US Highway 50, as well as strong increase in avalanche risks. Precipitation also reached over the Sierra Nevada into the southwestern part of the US with significant snow accumulations below 30 cm in the higher desert regions of Arizona, Nevada, and Utah.
5 day change in snow water equivalent
in inches in the Sierra Nevada 12.12.2022,
source:
CNRFC
|
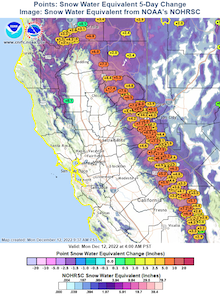 |
Earlier in November the Sierra Nevada was hit by the first significant snow systems of the winter season 2022/23, leading to an already significant snowpack in higher altitudes. The recent snowstorm led to another significant increase of the snowpack in the Sierra Nevada, with increases in the snow-water-equivalent of up to 200 mm.
The snowpack anomaly grew up to 250 % of the season-average up to date, reducing drought concerns in California, as the snowpack of the Sierra Nevada is essential for the fresh water supply of the state. Yet, a lot more snow has to fall to reach the seasonal average.
Text: KG
December 14, 2022
|