|
A very potent atmospheric river event impacted California from February 29, 2024, to March 04, 2024, bringing abundant precipitation to the state with storm-related precipitation totals reaching more than 250 mm. At higher elevations, the powerful storm brought extreme snowfall, leading to multiple meters of fresh snow accumulation.
The past winter season 2022/23 brought record-breaking snowfall to parts of the Sierra Nevada, bringing one of the largest snowpacks of the last decades in the state. This brought an end to the exceptional drought affecting the state of California since the beginning of the millennium. The start of the winter season 2023/24 was very slow, on January 01, 2024, the snowpack of the Sierra Nevada was only a low 28 % of the season-to-date average normally observed on January 01.
|
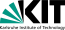
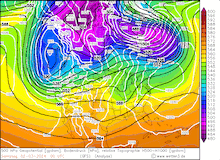
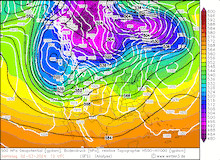
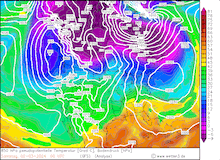
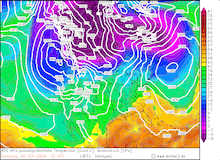
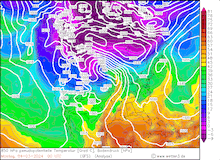
500 hPa Geopotential and sea surface pressure over North America, 29.02.2024 12 UTC - 04.03.2024 00 UTC, source:
wetter3
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
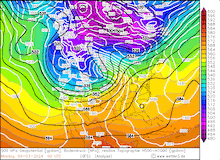 |
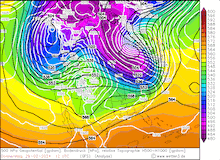
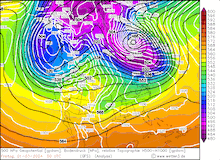
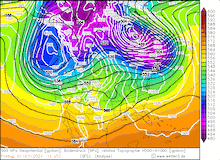
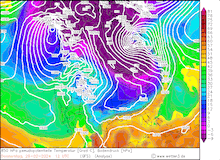
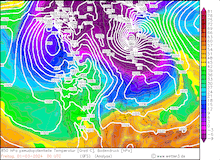
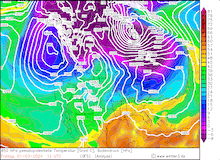
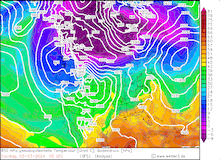
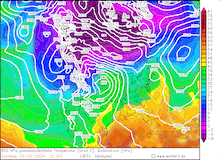
Since late January, multiple storm systems brought abundant snowfall to the Sierra Nevada, bringing the snowpack close to the season-up-to-date average. By late February, a strong outbreak of cold air masses from Northeastern Siberia led to the development of a strong trough over the Pacific Ocean off the coast of North America. The trough moved slowly eastwards over North America, advecting at the southern flank of the trough very moist air masses from the subtropical Pacific Ocean towards California.
|
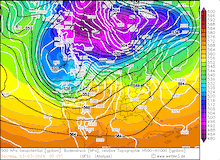
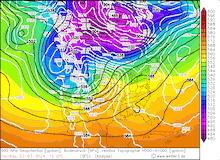
850 hPa pseudo-potential temperature and sea surface pressure over North America, 29.02.2024 12 UTC - 04.03.2024 00 UTC, source:
wetter3
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
In the US, this moisture transport from the subtropical Pacific Ocean is commonly referred to as a pineapple express. Because, when an atmospheric river is impacting California, often the satellite image shows a distinct cloud band originating in the vicinity of Hawaii and stretching to California. However, the current storm had a slightly different structure, accounting for the very potent outbreak of cold air masses originating from Siberia.
Typically, the most atmospheric rivers are very warm systems for the latitude and season. However, the current storm brought much lower snow levels during the event. Above 2000 m, all the precipitation of the storm fell as snow, leading to extreme snowfall both in duration and intensity. Along the Sierra Crest, extreme snowfall persisted for at least 72 h with violent storms along the peaks of the Sierra Nevada. Close to Lake Tahoe, wind gusts of up to 305 kph were observed, creating treacherous conditions. This wind gust is close to the record wind gust observed in the state of California, highlighting the severity of the storm system.
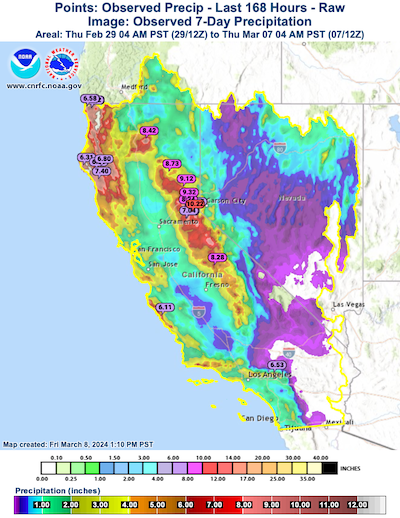
Along the Sierra Crest and in the northernmost Coastal Mountain ranges, radar-indicated 7-day precipitation totals show values of more than 250 mm, with most of this precipitation falling as snow. Especially in the region around the I80 corridor, the highest snow accumulations were observed, with multiple meters of fresh snow accumulation accumulating during the passage of the storm system. The extreme snowfall accompanied by white-out conditions due to the extreme winds at higher elevations led to treacherous traveling conditions along all roadways crossing the Sierra Nevada. Even I80 had to be closed for extended periods due to the extreme weather conditions along Donner Pass.
|
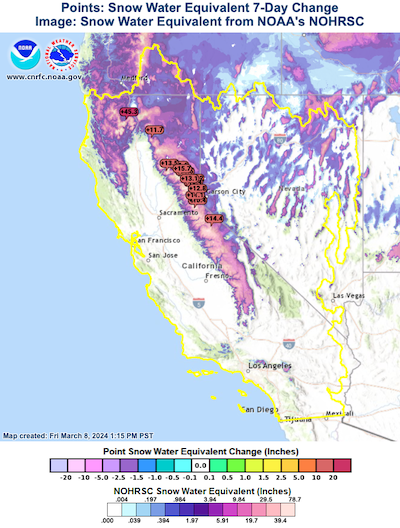
7-day accumulated precipitation radar-indicated and measurements (left) and 7-day change of the snow-water equivalent in California (right), 07.03.2024, source:
CNRFC
|
 |
 |
By March 01, 2024, the snow levels quickly fell to elevation beneath 1000 m, leading to large fresh snow accumulations even at elevations which are not usually accustomed to large fresh snow accumulations. On March 03, and March 04, 2024, the 850 hPa temperatures in the Northernmost parts of California dropped below -5 °C, more than 10 K below average in the region. Combined with the intense shower activity, snow flurries were observed in some coastal towns in Southern Oregon.
|
Snowpack of the Sierra Nevada measured by the snow water equivalent, 07.03.2024, source:
CDEC
|
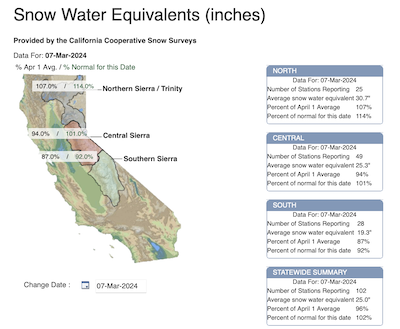 |
After the storm system had moved far enough eastwards, the snowfall receded on March 04, 2024. The snowpack of the Sierra Nevada, measured by the snow water equivalent, showed an astonishing recovery since the beginning of January. Throughout most of the Sierra Nevada, the snowpack is currently already close to the April 01 average. Only in the southern parts of the Sierra Nevada, the snowpack is still somewhat significantly below the April 01 average, sitting currently at 87 % of the April 01 average. Nevertheless, the recent precipitation likely ensured, that until the end of the current water year, California is not affected by another drought.
Text: KG
March 08, 2024
|